Magnetic resonance – many tools in one machine
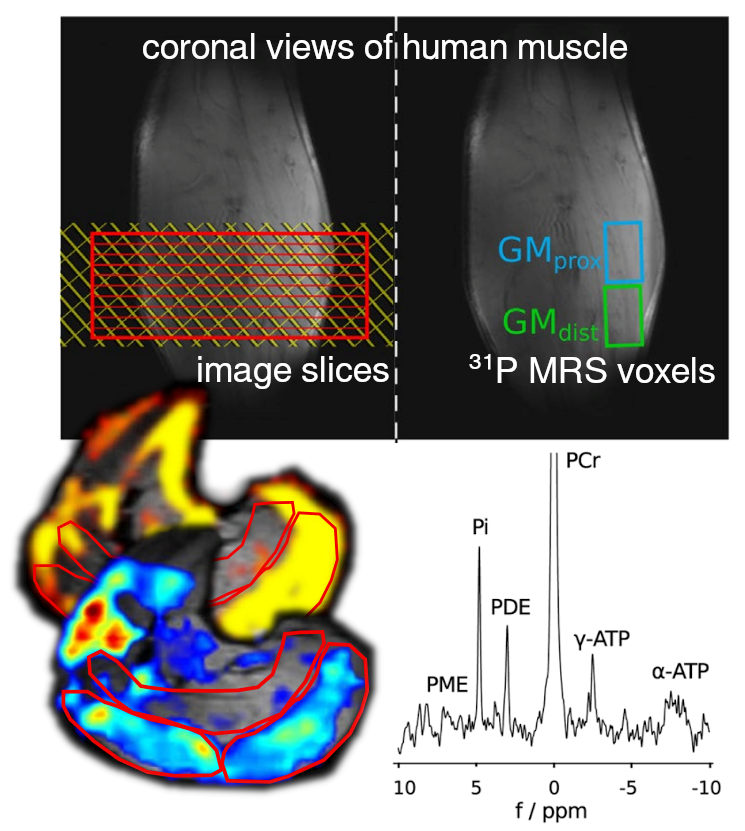
We like that „Nuclear Magnetic Resonance“ (NMR) can be used in so many different ways, on the same machine: MR spectroscopy can give time-resolved metabolic information by using the magnetic properties of hydrogen or other atomic nuclei that the human body consists of (e.g. ³¹P MRS uses phosphorus). Also MR imaging can deliver plenty of different information. For example, blood perfusion or elastic properties of tissue can be imaged, and many, many other types of contrasts are possible.
And what we like particularly: One can combine those things into a single measurement, and this is what we develop and investigate.
Research Area
Principal Investigator
Martin Meyerspeer
P +43 (0)1 40400-64610
Members
- Ariadna Cherit
- Georg Fiedler
- Anja Bernasch
- Philipp Faulhammer
- Roberta Frass-Kriegl
- Fabian Niess
- Marcos Wolf
- Quantifying Lactate and Energy Metabolism in Working Muscle (2022)
FWF (Austrian Science Fund), Stand-alone project - MR-Progression-Evaluation of Chronic Kidney Disease (2019)
FWF (Austrian Science Fund), Programm Klinische Forschung (KLIF) - Multimodal Magnetic Resonance Methods for Metabolic Research (2014)
FWF (Austrian Science Fund), Lead Agency Verfahren; ANR/Frankreich - Multi-nuclear in vivo MR spectroscopy at ultra-high field (2010)
FWF (Austrian Science Fund), Erwin-Schrödinger-Auslandsstipendien
Selected peer-reviewed publications
-
Cap V, Rocha Dos Santos V, Repnin K, Červený D, Laistler E, Meyerspeer M, Frass-Kriegl R. Combining Dipole and Loop Coil Elements for 7 T Magnetic Resonance Studies of the Human Calf Muscle. Sensors, 24(11), p. 3309.
-
Wolf M, Darwish O, Neji R, Eder M, Sunder-Plassmann G, Heinz G, Robinson SD, Schmid AI, Moser EV, Sinkus R, Meyerspeer M. Magnetic resonance elastography resolving all gross anatomical segments of the kidney during controlled hydration. Front Physiol. 2024 Feb 7;15:1327407.
-
Niess F, Roat S, Bogner W, Krššák M, Kemp GJ, Schmid AI, Trattnig S, Moser E, Zaitsev M, Meyerspeer M. 3D localized lactate detection in muscle tissue using double-quantum filtered 1 H MRS with adiabatic refocusing pulses at 7 T. Magn Reson Med. 2022 Mar;87(3):1174-1183.
- Meyerspeer, M. et al., 2020. 31P magnetic resonance spectroscopy in skeletal muscle: Experts’ consensus recommendations. NMR in Biomedicine 2020;e4246.
- Meyerspeer M, Magill AW, Kuehne A, Gruetter R, Moser E, Schmid AI. Simultaneous and interleaved acquisition of NMR signals from different nuclei with a clinical MRI scanner. Magn Reson Med 2016(5);76:1636–1641.
- Meyerspeer M, Robinson S, Nabuurs CI, Scheenen T, Schoisengeier A, Unger E, Kemp G, Moser E. Comparing localized and nonlocalized dynamic 31P magnetic resonance spectroscopy in exercising muscle at 7T. Magn Reson Med 2012;68(6):1713–1723.
- Niess, Fabian, "Magnetic Resonance Pulse Sequence Development for Interleaved Multimodal and Multinuclear Data Acquisition at 7 Tesla" Dissertation, Medizinische Universtität Wien, 2019
- Fiedler, Georg Bernd, "Muscle specific in-vivo Quantification of Metabolism by Dynamic Phosphorus Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy", Dissertation, Medizinische Universtität Wien, 2018
- Niess, Fabian, "MR Pulse Sequence Development for Localized Dynamic Spectroscopy with 7T" , Diplomarbeit, Technische Universität Graz, 2015
- Meyerspeer, Martin "Localised, Dynamic Phosphorus-31 Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy of Human Skeletal Muscle at High Field", Venia Docendi (Habilitation) in Medizinischer Physik, Medizinische Universtität Wien, 2016


